 NJ Foundation for Aging is honored that the North Jersey Alliance of Age-Friendly Communities, a partner organization, wrote about their impressions of our 22nd annual conference and shared them with us as a guest blog.
NJ Foundation for Aging is honored that the North Jersey Alliance of Age-Friendly Communities, a partner organization, wrote about their impressions of our 22nd annual conference and shared them with us as a guest blog.
Mornings on the golf course. Weekends with the grandkids. Vacations to dreamed-of destinations.
These are the visions of “successful aging” in many people’s minds, reflections of the one-dimensional view of growing old that is all too pervasive in our culture.
Not that those pretty images of retirement life aren’t experiences that people should desire. But without taking a deeper look at all the potential challenges and opportunities of growing older, many individuals will fail to anticipate later-in-life needs and desires.
In its advocacy work, the New Jersey Foundation for Aging routinely seeks to widen the lens that society trains on the lives and livelihoods of older adults, and the organization’s annual conference this year succeeded in doing just that.
Titled “2020 Vision for Successful Aging,” the conference, held virtually on Aug. 13 and 14, featured presentations on how aging intersects with a range of other policy issues from climate change to LGBTQ rights to immigration policies.
The conference also sought to open attendees’ eyes to the ways in which ageism is so widely normalized and internalized that it can often lead to us making uninformed individual and societal decisions that limit older adults’ choices in later years.
LONGEVITY COSTS
In a keynote address, Cynthia Hutchins, director of financial gerontology for Bank of America Merrill, said people shouldn’t avoid thinking about uncomfortable questions such as how long they might live and whether they will need some form of caregiving at some point.
“Longevity has changed the way we plan for our health and our health-care needs,” Hutchins said.
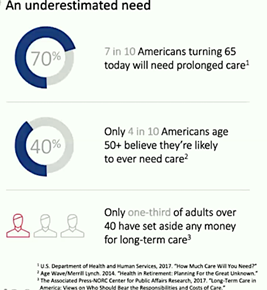
Previous generations didn’t envision living decades in retirement, but Baby Boomers and the generations that come after them will need to have a better understanding of such things as the limits of Medicare, the different options for long-term care, and how the financial and lifestyle choices they make early on can affect future health and happiness, Hutchins said.
In her presentation, Hutchins pointed out that, although one’s future health might be an unknown, there are useful projections individuals need to be aware of, such as that out-of-pocket health care costs between the ages of 65 and 80 can equal $114,000, and then grow to $247,000 by age 90 and $458,000 by age 100.
Figures like these might seem unbelievable to the average individual, but failing to adequately discuss and plan for future scenarios is what often leads to individuals having inadequate plans, and our government institutions having inadequate policies for the aging of the population.
At the root of our society’s unpreparedness for aging is often ageism, which includes the “prejudice against our future selves” that many of us possess.
Ageism was a focus of several workshops at the two-day conference, some of which examined how it can evolve into elder abuse or translate into a lack of advocacy on key issues that older adults and their advocates should be speaking about more often.
CLIMATE CHANGE + AGING
Climate change is foremost among those issues. Often portrayed as an issue of more concern to younger people worried about the future, what’s often overlooked is the fact that older people are the ones who tend to suffer the most harm from the severe storms and climbing temperatures that are already the result of our warming planet.
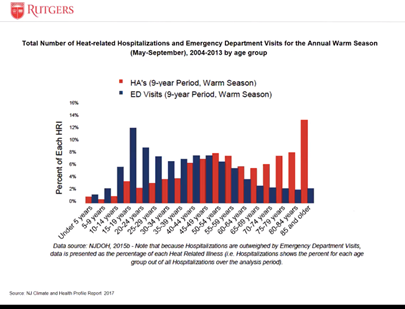 Jeanne Herb of the New Jersey Climate Change Resource Center at Rutgers University shared data showing that older people are at more risk of heat-related hospitalizations and more likely to have chronic conditions exacerbated by severe weather and the power outages and service interruptions that can result from them.
Jeanne Herb of the New Jersey Climate Change Resource Center at Rutgers University shared data showing that older people are at more risk of heat-related hospitalizations and more likely to have chronic conditions exacerbated by severe weather and the power outages and service interruptions that can result from them.
Similarly, older adults and their advocates need to be aware of how immigrants and people in the LGBTQ community are subject to more discrimination and barriers to housing and supportive services as they age, other panelists at the conference argued.
AGEISM/STEREOTYPES
In addition, the coronavirus pandemic has brought to light the way ageism, and bias toward disenfranchised groups, can lead to alarming disparities in disease exposure and treatment outcomes and to the many gaps and weaknesses in New Jersey’s long-term care systems, many speakers pointed out.
Organizers of the conference hoped that it would serve as a call to action, and ideas were shared on how to combat ageism with intergenerational programming and through the arts.
Katie York, director of Lifelong Montclair and the township’s senior services department, described the results of a study she helped guide on how performing arts programs can help lessen age stereotypes among young and old.
 The study entailed recruiting 72 individuals – ranging in age from 20 to 82 – to perform in skits that reflected age stereotypes. Afterward, participants were surveyed on whether the performances had altered their perceptions of aging and generational differences.
The study entailed recruiting 72 individuals – ranging in age from 20 to 82 – to perform in skits that reflected age stereotypes. Afterward, participants were surveyed on whether the performances had altered their perceptions of aging and generational differences.
As director of Lifelong Montclair, a now-five-year-old age-friendly community initiative, York said she has come to “recognize the need for culture change as a foundational element of age-friendly efforts.
“As more people understand the scope and value of our work on culture change, I believe our work will be that much more significant, and those battles we face along the way will be that much easier,” York said.
Julia Stoumbos, director of aging-in-place programs for The Henry & Marilyn Taub Foundation, said the NJFA conference provided many useful insights into how the leaders of age-friendly communities can help change views of aging, and also the steps that community leaders take to support the goal of aging in comfort, dignity, and safety.
“Often, the approach that communities take in addressing the needs of older adults is compartmentalized. There’s a big emphasis on leisure and recreation – planning Zumba classes and bus trips to Atlantic City. There’s also a tendency to medicalize old age, with programs focused on how to combat it or treat it like a disease.” ~ Julia Stoumbos, director of aging-in-place programs for The Henry & Marilyn Taub Foundation
“Often, the approach that communities take in addressing the needs of older adults is compartmentalized,” Stoumbos said. “There’s a big emphasis on leisure and recreation – planning Zumba classes and bus trips to Atlantic City. There’s also a tendency to medicalize old age, with programs focused on how to combat it or treat it like a disease.
“Those narrow approaches can sometimes lead to older adults being treated as if they are separate from the rest of the community, as if they are less invested in issues that affect all people at all ages,” Stoumbos said.
“Older adults have no less of a stake in the major issues of the day. They need to be empowered to stay engaged on these subjects, and communities need to make sure they are bringing the generations together in conversations about the weighty issues that affect quality-of-life for all.”
The age-friendly movement was first envisioned by the World Health Organization in 2005 as a way to find local strategies to prepare for the global challenges and opportunities of an aging population. The North Jersey Alliance of Age-Friendly Communities is supported by The Henry & Marilyn Taub Foundation and the Grotta Fund for Senior Care. Together those foundations are funding age-friendly initiatives in 16 communities in five counties – Bergen, Essex, Morris, Passaic and Union – which together have a population of more than a half-million people. The alliance also works in partnership with NJFA, AARP New Jersey, New Jersey Future and Rutgers University.

